A Company and Its Characteristics
What is Company?
A Company is an artificial entity created by a law that is distinct from its members and has the ability to carry a business in its own name.
A Company can sue and can be sued, can borrow money, can open a bank account, has a common seal, etc. Since it’s created by an act of law, it can only be dissolved by law. It has perpetual succession, independent of its members. Members can come and go but a company remains.
According to Section 3 (1) of the Indian Companies Act 1956
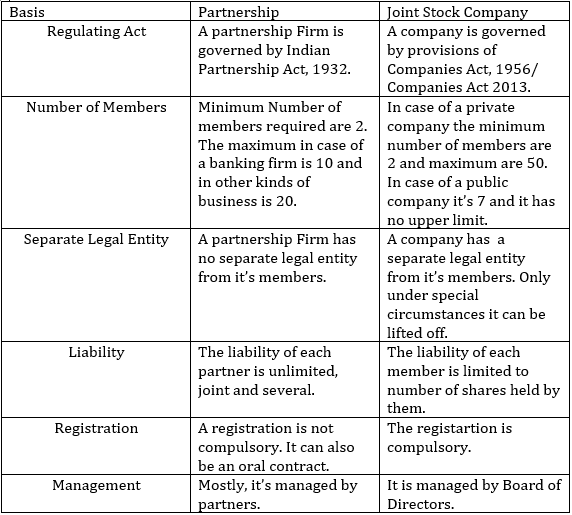
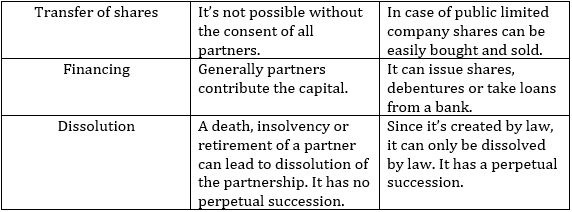
Difference between Partnership and Joint Stock Company
Features or Characteristics of a Company:
Artificial Person:
A company can come into existence through law. Since it’s created by law and has no physical form so it is called an artificial person. Although it has rights like a natural person, it can enter into contracts in its own name, it can sue and be sued, it can lend or borrow money, can hold properties in its own name. It can not cast its vote in an election.
Perpetual Succession:
Since it’s created by law, death, retirement, or insolvency of a member has no effect on the existence of the company. Members can come and go but a company remains.
Limited Liability:
The liability of each member is related to the number of shares held by a member. It can not be greater than that.
Common Seal:
A common seal acts as a signature of a company. All contracts undertaken by a company have its seal on them.
Transfer of Shares:
A share of a company can be bought or sold on Stock Exchange. It’s easily transferrable.
Board of Members:
A company has a board of members which undertakes its day-to-day functioning. A board of members enters into a contract on behalf of a company. They are elected by shareholders for the smooth running of a company.
Dissolution:
Since it is brought to life by an act of law, it can only be dissolved by an act of law. A lot of legal formalities need to be created to dissolve a company.
Chapter 1 – Accounting for Share Capital
- Company and its Characteristics
Company formation - Kinds of Companies
- Share Capital of a Company
- Nature and Classes of Shares
- Issue of Shares
- Accounting Treatment
- Forfeiture of Shares