In Balance of Payment class 12 Economics notes, we will study about the meaning of balance of payment, Structure of balance of payment, its components, its relationship with the foreign exchange rate, deficit in balance of payment account, etc….
The government keeps a record of all the transactions of the country with the rest of the world during a given period. This record of transactions is known as Balance of Payments (BOP).
Introduction of Balance of Payments – Economics Notes Class 12
What is Balance of Payments ?
Balance of Payments is an accounting statement , that provides information regarding all the economic transactions , between , the residents of a country, and rest of the world , during a given period. The period is usually one fiscal or financial year.
BOP is a flow concept as it is measured over a period.
BOP is prepared using the ‘DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM’. All the inflows are recorded on the credit side whereas all the outflows on the debit side.
Who are included in Resident ?
Resident of a country include : –
- An individual ;
- Firm ; or
- Government agencies.
A resident does not include foreign military personnel, tourists, migratory workers, branches of foreign countries, etc, even though they may work within the domestic territory of a country .
What are the economic transactions?
The transactions involve transfer of title or ownership of goods, services, assets or money are called Economic Transactions . Economic transactions can be classified as follows:
-
- Visible Items: These includes all type of physical goods , which are imported or exported, and which can be seen, touched and measured. For example, mobile phones, agricultural produce, fertilizers etc.….
- Invisible Items: These includes all type of services which cannot be seen, touched and measured but can only be felt. For example, banking, insurance, etc….
- Unilateral Transfers: These includes gifts, grants and other one- way transactions which does not involve the repayment in present or future. For example, scholarships, parents sending money to child, etc….
- Capital Transfers: These includes capital receipts which could be by way of purchase or sale of assets, borrowing or lending etc. For example, purchasing shares of foreign company, loan taken by Indian companies from foreign banks etc….
STRUCTURE OF BALANCE OF PAYMENT (BOP) – BALANCE OF PAYMENTS CLASS 12 NOTES
Balance of payment account follows the “double entry system” of accounts for recording the transactions in the books of accounts with the rest of the world. BOP account has two sides-
- Credit side: It records all the inflows or sources of foreign exchange.
- Debit side: It records all the outflows or uses of the foreign exchange.
As per the double entry system of accounts, the balance of payments account needs to be balanced. But this does not stand true in economic terms. In economic sense, the balance of payment account may not always be balanced. It could be surplus or deficit. This gives rise to three types of BOP:
- Balance BOP: It is when all the receipts of foreign exchange are equal to the payments of the foreign exchange.
- Surplus BOP: It is when the receipts of foreign exchange are more than the payments of the foreign exchange.
- Deficit BOP: It is when the receipts of foreign exchange are less than the payments of foreign exchange.
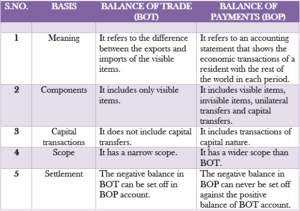
BALANCE OF TRADE (BOT)
Balance of trade refers to the difference between the amount of exports and imports of the visible items (goods only).
Balance of trade is a part of balance of payments account and it plays an important role in showing the overall situation of the balance of payment account. Balance of trade is also known as ‘Balance of visible Items’ or ‘Trade Balance’.
Balance of trade account can have a negative or positive balance.
- Surplus BOT: It is when the exports are more than the imports. This reflects a positive balance in BOT account.
- Deficit BOT: It is when the imports are more than the exports. This reflects a negative balance in BOT account.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN BOP & BOT – BALANCE OF PAYMENTS CLASS 12 NOTES
COMPONENTS OF BALANCE OF PAYMENT ACCOUNT
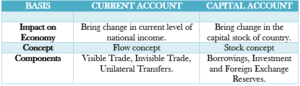
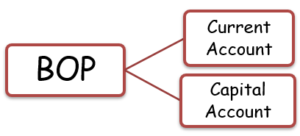
Balance of payment account can be broadly classified into two types of account: Current Account and Capital Account.
CURRENT ACCOUNT
It refers to an account which records all the transactions relating to export and import of goods and services and unilateral transfers during a given period.
It contains the receipt and payments of visible goods, invisible goods and unilateral transfers.
Components of Current Account:
- Export and import of goods: It include the visible goods that can be seen and touched. Payments are shown on the debit side (negative side) and receipts are shown on the credit side (positive side). The balance of this is also known as trade balance.
- Export and import of services: It include the invisible goods that cannot be seen or touched but only be felt. Payments of services are recorded on the debit side (negative side) and receipts are recorded on the credit side (positive side).
- Unilateral transfers: These are the one- way transactions. They include gifts, donations and other remittances. Payments are shown on the debit side (negative side) and receipts are shown on the credit side (positive side).
- Income receipts and payments to and from abroad: It includes income from investment. For example, income from rent.
Current account records all the receipts and payments of goods and services that affect the income and output of the economy. Thus, it shows the net income of the economy generated from the foreign sector.
BALANCE ON CURRENT ACCOUNT:
The credit and debit side of the current account gives the net value as the debit or credit balance.
If there is a credit balance in current account, it means there are more receipts than payments of foreign exchange. This shows the surplus in current account.
If there is a debit balance in current account, it means there are more payments than receipts of foreign exchange. This shows the deficit in current account.
CAPITAL ACCOUNT
It refers to the account which records all those transactions between the normal resident and the rest of the world which affects the assets and liabilities of the normal resident. However, it does not have any direct impact on the income and output level of the economy.
Components of Capital Account:
- Borrowings: It includes all transactions related to borrowings and lending to/from abroad. The receipts of loans and repayments of loan by the foreigners is recorded on the credit (positive) side. The lending to abroad and the repayment to abroad by the private sector is recorded on the debit (negative) side.
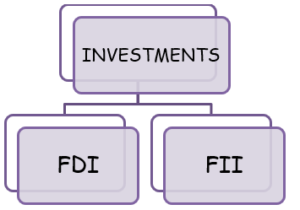
- Investments: It includes the investment done by the foreigners or the private sector. Investment by foreigners in India are recorded on the credit (positive) side. Investment by the Indian residents in foreign companies is recorded on the debit (negative) side
-
- FDI or Foreign Direct Investment: It refers to purchase of asset by giving up the whole control of it. For example, Purchase of land and building.
- FII or Foreign Institutional Investment: It refers to purchase of asset by not giving up the entire control of it to the purchaser. It is also known as Portfolio Investment. For example, Purchase of shares.
- Change in Foreign Exchange Reserve: The foreign exchange reserves are the financial asset of the government. Withdrawals from reserve are recorded on the credit (positive) side. Additions to the reserves are recorded on the debit (negative) side.
BALANCE ON CAPITAL ACCOUNT:
The transactions which lead to inflow of foreign exchange are recorded on the credit (positive) side. The transactions which lead to outflow of foreign exchange reserve are recorded on the debit (negative) side. If the credit side is more than the debit side, we get surplus in capital account. If the debit side is more than the credit side, we get deficit in capital account.
A deficit in the current account is settled by a surplus on the capital account.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CURRENT AND CAPITAL ACCOUNT
AUTONOMOUS AND ACCOMMODATING ITEMS
The transactions in balance of payment can be categorized as autonomous and accommodating.
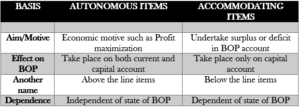
Autonomous Items: These are “above the line items.” They take place due to some economic motive such as profit maximization. They are independent of the state of BOP account. They take place on both current and capital accounts.
Accommodating Items: These are called “below the line items.” They take place to cover the deficit or surplus in BOP account. They are dependent of the state of BOP account. They take place only on capital account.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ACCOMMODATING AND AUTONOMOUS ITEMS
DEFICIT IN BALANCE OF PAYMENT ACCOUNT
It refers to a situation when the outflow on account of autonomous transactions are more than the inflow on account of such transactions.. A deficit creates problem as it is very difficult to cope up with. This causes disequilibrium in balance of payment account.
In such situation, official reserve transaction are used by the central bank to withstand the situation.
CBSE Economics Class 12 Notes Term I Syllabus
Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics
- Money and Banking Class 12 Notes
- Government Budget and the Economy Notes
- Foreign Exchange Rate Notes
Part B: Indian Economic Development
Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991:- 12 Marks
- Indian Economy on the eve of Independence Notes
- Indian Economy (1950-90) Notes
- Economic Reforms since 1991 Notes
Current challenges facing Indian Economy – 10 Marks