Forms of market Class 11 Notes
There are many different kinds of markets that can be in operation in a larger market area like ours. Because India is populated by a wide range of individuals with varying tastes and preferences, entering the Indian market results in a wide range of outcomes. As a result, various forms of the market locate our nation’s optimal location for success.
There are numerous markets with a high number of buyers and fewer sellers. Incredibly! There are also a lot of sellers, but only one buyer! In this section, we will investigate these amazing markets. Let us now move on to the different types of markets.
Market
Market refers to the entire region where buyers and sellers of a product come into contact with each other and influence the purchase and sale of the product.
- A market is a location where two parties can meet to make the sale and purchase of goods and services easier.
- Usually, buyers and sellers are the parties involved.
- A market can take the form of a physical location, such as a retail store, where sellers and buyers can meet face-to-face, or it can take the form of a virtual location, such as an online market, where there is no direct physical contact between buyers and sellers.
- The term “market” is used in a lot of contexts, like the securities market or the typical physical market, where people come together to buy and sell things.
Substantial components of the market are;
- Area: Market has nothing to do with any specific location. It covers a large area. Buyers and sellers eventually come together in the area.
- Buyers and sellers: Both sellers and buyers ought to communicate with one another. However, physical presence is not always implied by contact.
- Commodity: There must be a product that buyers and sellers will sell and buy in order for there to be a market.
- Competition: In order for a market to exist, buyers and sellers must compete with one another; otherwise, different prices may be charged for the same product.
Market structure
The market structure represents the number and type of firms in practice in the industry.
The key determinant of the market structure is;
- Number of buyers and sellers- The number of buyers and sellers on a commodity market indicates their influence on the commodity’s price.
- Nature of the Commodity- The commodity is sold at a uniform price if it is of homogeneous nature, or identical in every way. However, prices may vary if the product is of a different nature, such as toothpaste of different brands.
- The freedom of movement of firms- Price will remain stable in the market if firms can enter and exit freely.
- Knowledge about the market conditions- A uniform price prevails in the market if buyers and sellers are completely aware of the market conditions.
- Mobility of goods- In a market with uniform prices, the production factors can freely move from one location to another.
Perfect competition among Forms of market
Perfect competition is a market situation in which a very large number of buyers and sellers sell the same product at a price set by the market.
- The price is determined by the industry and not by any particular firm.
- A type of market in which a lot of people buy and sell the same thing is called this.
- The forces of market supply and market determine the price of a homogeneous product that is sold. Price is not something that can be changed by a single buyer or seller.
Characteristics of perfect competition:
- A very large number of buyers and sellers- There are a large number of buyers and sellers in a perfectly competitive market, but only a small amount of supply in the market.
Implication: Because a single buyer’s share of the total demand on the market is so insignificant, the buyer cannot change his demand to affect the market price. A high number indicates that a single seller or buyer is not successful in influencing the current market price on its own.
- Homogeneous product- A homogeneous product is one in which there is no differentiation at all.
Implication: Therefore, each company’s product is an excellent replacement for the other. There are zero degrees of market control or monopoly control when there is no differentiation in the products sold. As a result, the lowest possible price prevails in the marketplace.
- Freedom of entry- In perfect competition, there is freedom of entry and exit in the market.
Implication: The freedom of movement of firms signifies that firms in the long run will be able to earn only normal profit and bear normal losses only.
- Perfect knowledge among buyers and sellers- Buyers and sellers are completely aware of the current market price. They are also aware that the market is stocked with identical products. As a result, the producer can’t charge different prices to different buyers from the market. Price discrimination is not allowed to result in high profits.
- Perfect mobility of factors of production- Perfect mobility means that production factors can move anywhere. They’ll go into that business where they can get good prices. As a result, the market is dominated by a uniform factor price.
- No transportation cost- Purchasing a product from one seller rather than the other incurs no additional transportation costs. It prevents any manufacturer from raising the price of the product.
- Independent decision-making- No agreement exists between businesses regarding the quantity to be produced or the price to be charged. In comparison to any other kind of market, perfect competition makes it possible to produce the most at the lowest price
Firm- Price taker under Forms of market
- A price taker means that a specific firm has no choice but to sell at the price set by the industry in perfect competition
- Each firm is a small component of the marker, and the output of one firm can perfectly substitute for that of another firm. These points suggest that no business can unilaterally alter the market price at which it can sell its products or services. The term “price taker” refers to it because it must accept the market equilibrium price or “take” it.
- Individual firms cannot affect the price by themselves because their share in the overall market supply is insignificant.
- It does not play a role in determining price and can’t affect supply rather than demand in the market.
- Industry determines the price, where the market demand curve intersects the market supply curve.
Demand curve under Forms of market
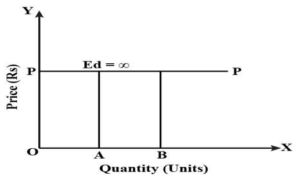
- The market demand curve for goods and services in a perfectly competitive market is a straight line, parallel to the x-axis. However, no single firm in this market can influence the price at which it sells its output. This point means a firm that is a price taker must take the equilibrium market price as given, and the firm faces a perfectly elastic demand.
- A perfectly competitive firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve in a perfectly competitive market.
- A perfectly competitive firm’s demand curve is a horizontal line at the market price. This result means that the price it receives is the same for every unit sold. The marginal revenue received by the firm is the change in total revenue from selling one more unit, which is the constant market price. So a perfectly competitive firm’s demand curve is the same as its marginal revenue curve.
- Under perfect competition, MR = AR
- A firm’s total profit is maximized by producing the level of output at which marginal revenue for the last unit produced equals its marginal cost or MC. In a perfectly competitive market, MR is equal to the market price for all levels of output. These points imply that a perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing output where P = MC.
Forms of market class 11 notes give a wholesome definition of supply and various related concepts. These notes also provide the factors affecting the price elasticity of demand. You can stay active and engaged throughout your reading, revision, and lectures by taking these notes. Additionally, they aid in clear thinking and comprehension. Selectively identify important ideas. A useful record of important information and its sources can be found in these notes. These notes will help you remember what you heard better.