Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs, covers certain important topics, which are covered under syllabus for ISCE Class 12 and are coming in Term I examination for the academic year 2022-23. Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs Test contains 62 questions. MCQ on Economics Class 12 ISC have been made for Class 12 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
1. A study in the relationship between inputs and output is known as
(a) Theory of Returns
(b) Theory of Scale
(c) Theory of Factors
(d) Theory of Production
Answer
Answer: (d) Theory of Production
2. A study of relationship between outputs and cost of production is known as
(a) Theory Of Costs
(b) Theory of Return
(c) Theory of Factors
(d) Theory of Scale
Answer
Answer: (a) Theory Of Costs
3. In economics, production refers to the act of making goods and services and thereby adding _________ to the object
(a) cost
(b) Usefulness
(c) Utility
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (c) Utility
4. In economics, Production means the creation of ____.
(a) Benefit
(b) Value
(c) Money
(d) Utility
Answer
Answer: (d) Utility
5. The act of making goods and services and adding utility to the object is called ___ in economics.
(a) Production
(b) Costing
(c) Selling
(d) Marketing
Answer
Answer:(a) Production
6. In Economics, Production includes
(a) Goods
(b) Services
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both A and B
7. The ‘Theory of Production’ provides the base for the _____.
(a)Theory of Demand
(b) Theory of Costs
(c) Theory of Supply
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Theory of Costs
8. Cost of Production depends upon
(a) The physical relationship between inputs and outputs
(b) Prices of the inputs
(c) Prices of the Outputs
(d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: (d) Both A and B
9. Economics define production in a ___ sense.
(a) Narrow
(b) Wider
(c) Moderate
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Wider
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
10. ____ is regarded as a part of production
(a) Transportation
(b) Trading
(c) Packaging
(d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: (d) Both A and B
Production Function
11.The relationship between inputs and outputs is known as
(a) Cost function
(b) input output function
(c) scale function
(d) production function
Answer
Answer: (d) production function
12.The production function shows the ______ number of inputs that are required to produce a certain level of output with the use of the best available techniques of production
(a) maximum
(b) minimum
(c) efficient
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) minimum
13. Production Function is expressed with reference to a ________
(a) particular period of time
(b) physical relationship between inputs and outputs
(c) technological relationship
(d) All of the Above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the Above
14. Production Function is a ______ Variable
(a) Dependent
(b) independent
(c) unaffected
(d) constant
Answer
Answer: (a) Dependent
15. ____ process involves the use of various inputs to produce output.
(a) Costing
(b) Production
(c) Construction
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Production
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
Short Run and Long Run
16.________ refers to the period of time during which the number of fixed factors cannot be changed
(a) Production Run
(b) Short Run
(c) Long Run
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (b) Short Run
17. Long Run refers to the time period during whichall Factors of production are _______
(a) fixed
(b) Constant
(c) variable
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) variable
18. In Production Function equation Qx = f(f1 + f2 + f3……,fn), Qx stands for
(a) Input
(b) Output
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Output
19. In Production Function equation Qx = f(f1 + f2 + f3……,fn), f1 stands for
(a) Input
(b) Output
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Input
20. In production function Qx is
(a) Independent Variable
(b) Dependent Variable
(c) Constant Variable
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Dependent Variable
21. In production function f1 + f2 + f3……,fn are
(a) Independent Variable
(b) Dependent Variable
(c) Constant Variable
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Independent Variable
22. If we assume there are only two inputs, namely labour (L) and Capital (K) , then the production function will be
(a) Qx = f(L,L)
(b) Qx = f(L,K)
(c) Qx = f(K,K)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Qx = f(L,K)
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
Types of Production Function is CANCELLED FROM ISC SYLLABUS
Total Average and Marginal Physical Product
23. Total Product is also known as
(a) Total Factor
(b) Total Returns
(c) Marginal Return
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (b) Total Returns
24.AP refers to the ________ of a variable factor
(a) total output
(b) output per unit
(c) change in TP
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (b) output per unit
25.________ is the change in TP resulting from the use of one additional variable factor.
(a) MP
(b) TP
(c) AP
(d) MVC
Answer
Answer: (a) MP
26.The formula to calculate Average Product is:
(a) AP = TP/L
(b) AP = L/TP
(c) AP = MP/L
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) AP = TP/L
27. If TP is 360 and workers employed for production are 3. Calculate AP.
(a) 100
(b) 120
(c) 140
(d) 160
Answer
Answer: (b) 120
28.The formula to calculate Marginal Product is:
a) MP = TP/L
(b) MP = ΔAP/L
(c) MP = ΔTP/L
(d) MP = AP/L
Answer
Answer: (c) MP = ΔTP/L
29. The formula to calculate Total Product is:
(a) TP = AP × L
(b) TP = ∑MP
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both A and B
30. If 2 workers produce 300 pens and 3 workers produce 450 pens, the marginal product of the third worker is:
(a) 100
(b) 150
(c) 200
(d) 250
Answer
Answer: (b) 150
31. If AP of 5 workers is 130, then what will be the TP
(a) 500
(b) 550
(c) 600
(d) 650
Answer
Answer: (d) 650
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
Relationship between TP, MP and AP
32. When MP > AP
(a) AP is falling
(b) AP is constant
(c) AP is max
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) AP is max
33. MP can be
(a) Positive
(b) Zero
(c) Negative
(d) All of the Above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the Above
34. When MP curve intersects AP curve, AP is
(a) maximum
(b) least
(c) going to start increasing
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) maximum
35. When the MP curve lies below the AP curve, AP
(a) Increases
(b) reaches 0
(c) declines
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) declines
36. When TP Increases at a _______ rate, MP declines
(a) Increasing
(b) constant
(c) decreasing
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) decreasing
37. When TP starts to decline, MP becomes
(a) positive
(b) 0
(c) max
(d) Negative
Answer
Answer:(d) Negative
Returns to Factor
38. Returns to a factor means change in the physical quantity of a good when the quantity of one factor is increased while that of the other factors ______
(a) increases
(b) Decreases
(c) remains constant
(d) becomes negative
Answer
Answer: (c) remains constant
39. ______ returns to factor refers to a situation in which additional units of a variable factor at the same amount of output
(a) Marginal
(b) Diminishing
(c) Constant
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Constant
40. When Marginal product of a factor falls as more and more of it is used, it’s known as
(a) Constant Returns to Factor
(b) Diminishing Returns to Factor
(c) Increasing returns to factor
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Diminishing Returns to Factor
41. In Increasing returns to factor TP and MP
(a )rise
(b) fall
(c) are constant
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) rise
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
Law of Variable Proportions
42. The Law of Variable Proportions is an extension of
(a) Law of Demand
(b) Law of Supply
(c) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(d) Law of Diminishing Returns
Answer
Answer: (d) Law of Diminishing Returns
43. The law of variable proportions states that as more and more units of a variable factor are applied to a given quantity of fixed factor, total product may increase at an increasing rate initially but eventually it will _____
(a)become negative
(b)increase at a diminishing rate
(c) Increase at an increasing rate
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) increase at a diminishing rate
44. Which of the following are assumptions of the Law of Variable Proportions?
(a) The state of technology is unchanged
(b) All variable factors are homogeneous
(c) some inputs are fixed while others are varied
(d)all of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all of the above
45. Increase in MP will pull up
(a) TP
(b) AP
(c)both the options
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer:(c) both the options
46. All 3 curves TP, MP and AP are ______ sloped initially and ______ sloped subsequently
(a)positive, negative
(b) negative, positive
(c) positive, positive
(d) negative, negative
Answer
Answer: (a) positive, negative
The Three Stages of Production
47. The point on the Total Product curve where level of MP is Maximum is called as
(a) Point of Satiety
(b) Point of Satisfaction
(c) Point of Returns
(d) Point of Inflexion
Answer
Answer: (d) Point of Inflexion
48. In the stage of increasing return, the curve starts at origin and ends when
(a)AP is maximum
(b) MP is Maximum
(c) TP is maximum
(d) all are at their max
Answer
Answer: (a) AP is maximum
49. During thestage of increasing returns ______ is positive throughout
(a) MP
(b) TP
(c) AP
(d)All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
50. In Stage 2, the total product ________ rate
(a) Increases at an increasing
(b) decreases at a decreasing rate
(c) Increases at a constant rate
(d)increases at a decreasing rate
Answer
Answer: (d) increases at a decreasing rate
Law of Returns to Factor and Returns to Scale Class 12 MCQs
51. The second stage of Diminishing Returns ends when
(a) AP is least
(b) MP is negative
(c)MP is 0
(d) AP is 0
Answer
Answer: (c) MP is 0
52. In the third stage of negative returns, MP is
(a) Constant
(b) 0
(c)negative
(d) positive
Answer
Answer: (c) negative
53.Identify this Curve
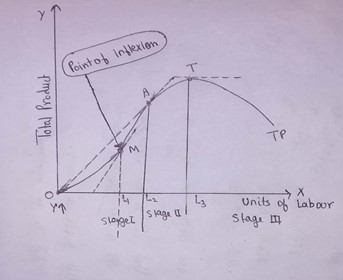
(a) MP
(b)TP
(c) AP
(d) Returns to scale curve
Answer
Answer: (b) TP
54.What stage is found between points A and L3
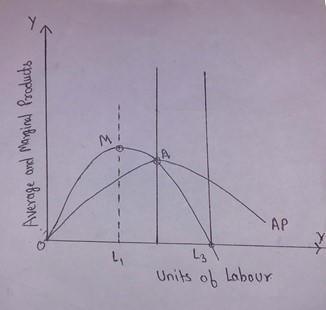
(a) Stage 1
(b) Stage 2
(c) Stage 3
(d) Stage of negative Returns
Answer
Answer: (b) Stage 2
Explanation of the Law of Variable Proportions
55. Which of the following are causes of increasing returns
(a) Fuller Utilisation of Fixed factors
(b) Increase in efficiency
(c) Both a and b
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Both a and b
56.As the number of variable factors increases in stage 1, efficiency of variable factor is increased due to
(a) overcrowding
(b) management problems
(c)specialization
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) specialization
57. Diminishing Returns to Factor are found due to
(a) overcrowding
(b) management problems
(c) Disruption of Optimum Proportion
(d) none off the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Disruption of Optimum Proportion
58. Factors of production are ______ of each other
(a) perfect substitutes
(b) compliments
(c)imperfect substitutes
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) imperfect substitutes
59. Overcrowding leads to ______ returns to factor
(a) constant
(b) Diminishing
(c) negative
(d) Positive
Answer
Answer: (c) negative
60.Management problem arises due to
(a) shortage of variable factor
(b) excess of variable factor
(c) increase in efficiency
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) excess of variable factor
STAGES OF OPERATION, DECISION TO PRODUCE AND RETURNS TO SCALE IS CANCELLED
61. When all inputs are changed in the same proportion, this is called change in _____ of production
(a) factor
(b) quantity
(c) scale
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) scale
62.change in output in the _____ is associated with change in scale of production
(a) short- run
(b) long-run
(c) both a and b
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) long-run
Economics Class 12 ISC MCQs – Term 1
- Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
- Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
- Elasticity of Demand
- Supply – Law of Supply and Price Elasticity of Supply
- Market Mechanism
- Law of Returns
- Cost and Revenue Analysis
- Forms of Market
- Producer’s Equilibrium
- Determination of Equilibrium Price and Output under Perfect Competition