Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ Questions covers certain important topics, which are covered under syllabus for ISCE Class 12 and are coming in Term I examination for the academic year 2022-23. Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ Test contains 41 questions. MCQ on Economics Class 12 ISC have been made for Class 12 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Marginal Utility Analysis and Utility
1.A consumer will be in equilibrium when he spends his given income on the purchase of different goods in such a way so as to maximize his ________
(a) Marginal Utility
(b) Demand
(c) Cardinal Utility
(d) Total Utility
Answer
Answer: (d) Total Utility
2.______ refers to the want satisfying power of a commodity
(a) Supply
(b) Demand
(c) Utility
(d) Indifference Curve
Answer
Answer: (c) Utility
3.Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of Utility
(a) Utility is Relative
(b) Utility is same as demand
(c) Utility is different from usefulness
(d) Utility is subjective
Answer
Answer: (b) Utility is same as demand
4. A consumer will be _______ when he spends his given income on the purchase of different goods in such a way to maximize his total utility
(a) satisfied
(b) in a state of rest
(c) in equilibrium
(d) all of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all of the above
5. A consumer will maximize his total utility when he allocates his income among various commodities in such a way that the _________ utility of the last rupee spent on each commodity is ______
(a) total, equal
(b) marginal, unequal
(c) marginal, equal
(d) Total, unequal
Answer
Answer: (c) marginal, equal
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Meaning of Utility – Total and Marginal
6. Utility refers to the _______ of a commodity
(a) price
(b) want-satisfying power
(c) weight
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) want-satisfying power
7. Since utility is _______, it cannot be measured in objective terms
(a) relative
(b) Subjective
(c) a power
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Subjective
8.Smoking a cigarette has harmful effects on a person, even after this, why does it possess utility.
(a) Utility is not measurable
(b) Utility is abstract
(c) Utility is different from usefulness
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Utility is different from usefulness
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Relationship between T.U and M.U
9. What is the formula for calculating M.U of nth term ?
(a) TU n + TU n+1
(b) TU n – TU n+1
(c) TU n – TU n-1
(d) TU n – TU n -1
Answer
Answer: (d) TU n – TU n -1
10. What is Point of Satiation
(a) Point at which TU Is maximum
(b) Point at which MU is least
(c) Point at which MU is maximum
(d) Point at which MU = TU
Answer
Answer: (a) Point at which TU Is maximum
11. When M.U keeps on decreasing, T.U increases as long as the M.U is
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) constant
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) positive
12. MU is 0 when,
(a) T.U is increasing
(b) T.U is decreasing
(c) T.U is max
(d) Both b and c
Answer
Answer: (c) T.U is max
Answer the following with reference to the given schedule
| Units of apples | Total Utility | Marginal Utility |
| 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
0
10 16 20 22 22 19 |
–
10 6 4 2 0 -3 |
13. After consuming how many apples is M.U equal to zero
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer
Answer: (c) 5
14.After consuming the 6th unit, why does the M.U become negative
(a) Because he has crossed his point of Satiety
(b) Because his taste changed
(c) because the size of the mango increased
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Because he has crossed his point of Satiety
15. M.U is positive but decreases when T.U
(a) increases at an increasing rate
(b) Decreases
(c) is 0
(d) Increases at a diminishing rate
Answer
Answer: (d) Increases at a diminishing rate
16.T.U is negative when
(a) M.U is 0
(b) M.U is negative
(c) T.U = M.U
(d) The statement is false
Answer
Answer: (d) The statement is false
17. Which one of these is NOT true about TU and MU
(a) TU in increases as long as MU is positive
(b) TU is maximum when MU is negative
(c) TU is maximum when MU is zero
(d) TU decreases when MU becomes negative
Answer
Answer: (b) TU is maximum when MU is negative
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
18. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that as amount consumed of a commodity ______, other things being constant, marginal utility _____
(a) increases, Decreases
(b) Increases, Increases
(c) decreases, decreases
(d) decreases, increases
Answer
Answer: (a) increases, Decreases
19.Which one of the following are assumptions about the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(a) All units of a commodity must be identical
(b) The utility is measurable
(c) There should be no change in taste of consumer
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
20. Which of these are exceptions to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(a) Desire for Money
(b) Food
(c) Water
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Desire for Money
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Consumer’s Equilibrium through Cardinal Utility
21. Consumer’s Equilibrium is attained when
(a) Marginal Utility of a Good is Maximum
(b) Marginal Utility of a Good is equal to Price of the good
(c) Marginal Utility of a good is less than Price of the good
(d) Consumer buys only one good
Answer
Answer: (b) Marginal Utility of a Good is equal to Price of the good
22. Given below is the Marginal Utility obtained by a consumer on purchasing the given number of units. If the price of the jacket is 650, at what quantity of shirts does the consumer obtain Equilibrium
| Units Of jacket | Marginal Utility in rupees |
| 1
2 3 4 5 |
750
700 650 600 550 |
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
Answer: (b) 3
23. If MUx > Px , a utility maximizing consumer will purchase _____ of the commodity
(a) more
(b) Less
(c) Same
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) more
Equi-Marginal Utility
24. The utility maximizing consumer must allocate his income among various commodities in such a way that the last unit of money spent on each commodity gives him the same Marginal Utility. Name this Law
(a) Law of Equi-Marginal utility
(b) Consumer Equilibrium Law
(c) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(d) Law of Equilibrium Satisfaction
Answer
Answer: (a) Law of Equi-Marginal utility
Indifference Curve Analysis
25. The indifference curve approach was fully developed by
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Alfred Marshall
(c) JR Hicks and RGD Allen
(d) Paul Samuelson
Answer
Answer: (c) JR Hicks and RGD Allen
26. ________ means that that Utility that a consumer gets from a commodity can be measured in absolute terms.
(a) Ordinal utility
(b) Indifference utility
(c) Cardinal Utility
(d) Scale of preference
Answer
Answer: (c) Cardinal Utility
27. A combination of how many goods are studied under Indifference Curve Analysis
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b) 2
28. ___________ refers to a tabular representation of various combinations of two goods that would give equal amount of satisfaction to the consumer
(a) Indifference Map
(b) Indifference Schedule
(c) Consumer equilibrium Curve
(d) indifference Curve
Answer
Answer: (b) Indifference Schedule
29. An indifference Curve is also known as
(a) ISO-Utility Curve
(b) Utility Curve
(c) Budget Line
(d) MRS curve
Answer
Answer: (a) ISO-Utility Curve
30. Which one of the following is not an assumption of Indifference Curve Analysis
(a) Subjectivity
(b) Rationality
(c) Transitivity of Choice
(d) Ordinal Utility
Answer
Answer:(a) Subjectivity
31. ___________ is the rate at which the consumer is willing to substitute one good for another without changing the level of consumption
(a) Marginal Opportunity Cost
(b) Marginal Utility
(c) Budget Allocation
(d) Marginal Rate of Substitution
Answer
Answer: (d) Marginal Rate of Substitution
32. Which one of the following is NOT a property of Indifference Curves
(a) An Indifference Curve slopes down from left to right
(b) Indifference Curves Intersect each other
(c) IC is convex to origin
(d) Higher IC yields higher satisfaction
Answer
Answer: (b) Indifference Curves Intersect each other
33. A high indifference curve shows a ______ level of satisfaction
(a) lower
(b) equal
(c) Higher
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Higher
34. Indifference Curves portray a combination of 2 goods which give the consumer ________
(a) no satisfaction
(b) equal satisfaction
(c) dissatisfaction
(d) utility
Answer
Answer: (b) equal satisfaction
35. Two indifference curves can never intersect each other since
(a) two indifference curves represent different amount of satisfaction
(b) a consumer’s satisfaction on consumption cannot be equal on two separate curves
(c) both of the above
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) both of the above
36. ________ shows various combinations of 2 commodities which can be purchased with a given budget at given prices of 2 commodities
(a) Marginal Rate of Substitution
(b) Budget Line
(c) Indifference Curve
(d) Budget Curve
Answer
Answer: (b) Budget Line
37. In the given Budget Line, if the price of Clothes is 80 rupees and that of food is 40, at any point, what is the total budget of the consumer
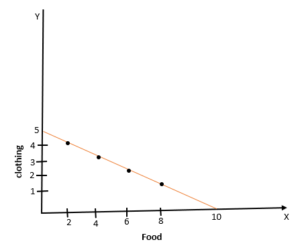
(a) 400
(b) 300
(c) 200
(d) 100
Answer
Answer: (a) 400
38. The budget line is
(a) positively sloped
(b) Parallel to Y axis
(c) has a slope equal to the negative price ratio of the two commodities
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) has a slope equal to the negative price ratio of the two commodities
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
Consumer’s Equilibrium through Indifference Curve Approach
39. Which of the following is a condition for consumers equilibrium
(a) MRS = Price Ratio of the 2 goods
(b) MRS of two goods should be equal to Px/Py
(c) MRS should be decreasing at equilibrium
(d) All of the Above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the Above
40.A consumer attains Equilibrium when
(a) He maximizes his total utility
(b) He buys goods within his budget
(c) He maximizes his utility, given his income and price of commodities
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (c) He maximizes his utility, given his income and price of commodities
41. An indifference curve above the budget line ________
(a) gives higher satisfaction to the consumer
(b) is unattainable to the consumer
(c) involves a higher combination of goods as compared to the lower curves
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Economics Class 12 ISC MCQs – Term 1
- Demand and Law of Demand MCQ Class 12
- Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 MCQ
- Elasticity of Demand
- Supply – Law of Supply and Price Elasticity of Supply
- Market Mechanism
- Law of Returns
- Cost and Revenue Analysis
- Forms of Market
- Producer’s Equilibrium
- Determination of Equilibrium Price and Output under Perfect Competition