Statistical Tools and Interpretation MCQs – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode Class 11 Economics are covered in this Article. Statistical Tools and Interpretation – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode MCQs Test contains 35 questions. Answers to MCQs on Statistical Tools and Interpretation – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode Class 11 Economics are available after clicking on the answer. These MCQ have been made for Class 11 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge. For more MCQ’s, subscribe to our email list.
Statistical Tools and Interpretation MCQs Class 11 Economics – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode
1. ______________ is most frequently observed data value
a) Arithmetic Mean
b) Mode
c) Median
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Mode
2. Mode of 1,2,3,4,4,5 is ________________
a) 4
b) 5
c) 2
d) 1
Answer
Answer: a) 4
3. Median is _____________ the Arithmetic Mean and Mode.
a) Always between
b) Always greater than
c) Always less than
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Always between
4. _____________ is used to describe Qualitative data.
a) Mean
b) Mode
c) Median
d) None
Answer
Answer: b) Mode
5. The algebraic sum of deviation of a set of n values from Mean is _______________
a) n
b) 1
c) 0
d) None
Answer
Answer: c) 0
6. Relative Magnitude of the Mean, Median, Mode is _____________
a) AM>Median<Mode / AM<Median>Mode.
b) AM>Median>Mode / AM>Median<Mode.
c) AM<Median>Mode / AM<Median<Mode.
d) AM>Median>Mode / AM<Median<Mode.
Answer
Answer: d) AM>Median>Mode / AM<Median<Mode.
7. For mode in continuous series, class intervals __________ be equal and series __________ be exclusive.
a) Should, can
b) Can, should
c) Should, should
d) Can, can
Answer
Answer: c) Should, should
8. Mode in continuous frequency distribution is _________.
a) Mode = L+(D1÷(D1+D2))*h
b) Mode = L*(D1÷(D1+D2))*h
c) Mode = L+(D1÷(D1+D2))%h
d) Mode = L-(D1÷(D1+D2))*h
Answer
Answer: a) Mode = L+(D1÷(D1+D2))*h
D1 stands for the Difference between the frequency of the modal class and the frequency of the preceding modal class.
D2 stands for the difference between the frequency of the modal class and the frequency of the succeeding modal class.
9. Mode of data 1,1,2,2,5,3,4,4 is __________________
a) 1,2,5
b) 1,2,4
c) 2,3,5
d) 3,4,5
Answer
Answer: b) 1,2,4
10. Most commonly used statistical measures of central tendency is _________
a) Mean
b) Median
c) Mode
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
11. Arithmetic Mean is equal to ____________________
a) Sum of values of observations / No: of observations
b) Half of values of observations x No: of observations
c) Sum of values of observations + No: of observations
d) Sum of values of observations % No: of observations
Answer
Answer: a) Sum of values of observations / No: of observations
12. Arithmetic Mean Is denoted by ____________

Answer
Answer: c) X̅
13. ________ is the positioned value of the variable which divides the distribution into two equal parts.
a) Mean
b) Median
c) Mode
d) None
Answer
Answer: b) Median
14. Median of 5,7,6,1,8,10,12,4 and 3 is ___________________
a) 5
b) 4
c) 6
d) 2
Answer
Answer: c) 6
15. Median of 25, 72, 28, 65, 29, 60, 30, 54, 32, 53, 33, 52, 35, 51, 42, 48, 45, 47, 46, 33 is __________________
a) 45.5
b) 55.4
c) 33.5
d) 63.5
Answer
Answer: a) 45.5
Statistical Tools and Interpretation MCQs Class 11 Economics – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode
16. __________ is the middle element when the data is arranged in the order of magnitude.
a) Mean
b) Mode
c) Median
d) Integrity
Answer
Answer: c) Median
17. Position of median is equal to ____________ item.
a) (N+1) / 2
b) (N-1) / 2
c) (N*(N+1)) / 2
d) None
Answer
Answer: a) (N+1) / 2
18. Q₁ is equal to size of ___________ item.
a) (N÷1) / 4
b) (N-1) / 4
c) (N+1)* 4
d) (N+1)/ 4
Answer
Answer: d) (N+1)/ 4
19. Q₃ is equal to size of ___________ item.
a) (N÷1) / 4
b) 3(N+1) / 4
c) (N+1)* 4
d) (N+1)/ 4
Answer
Answer: b) 3(N+1) / 4
20. What is the median income if position of the median is 10 th item?
| INCOME | No: of persons | Cumulative frequency |
| 10 | 2 | 2 |
| 20 | 4 | 6 |
| 30 | 10 | 10 |
| 40 | 4 | 20 |
a) 10
b) 30
c) 20
d) 4
Answer
Answer: b) 30
21. _________ concentrates on central items of data.
a) Mean
b) Median
c) Integral
d) Both A and C
Answer
Answer: b) Median
22. _________ are the measures which divides the data into four equal parts?
a) Mono
b) BI-parties
c) Quartiles
d) None
Answer
Answer: c) Quartiles
23. Q₁ and Q₃ denote two limits within which central __________of the data lies.
a) 50%
b) 75%
c) 25%
d) 100%
Answer
Answer: a) 50%
24. ______________ divides the distribution into 100 equal parts.
a) Quartile
b) Percentile
c) Median
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Percentile
25. _________ is the median value in percentile.
a) p₁₀₀
b) p₅₀
c) p₇₅
d) p₂₅
Answer
Answer: b) p₅₀
26. Calculate Q₁ from the data 22.26, 14.30, 14.30, 18.11, 35.41, 12.32 is _____________
a) 12
b) 13
c) 13.5
d) 13.75
Answer
Answer: c) 13.5
27. X̅ _________
a) (x₁ + x₂ + x₃+……………..+ xⴖ) ÷ n
b) (x₁ – x₂ – x₃-……………..- xⴖ) ÷ n
c) (x₁ * x₂ * x₃*……………..* xⴖ) ÷ n
d) None
Answer
Answer: a) (x₁ + x₂ + x₃+……………..+ xⴖ) ÷ n
28. X̅ = __________
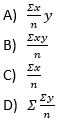
Answer
Answer: c) (∑x)/n
29. Calculate Mean of 40, 50, 55, 78, 58
a) 56.2
b) 65.4
c) 44.0
d) 33.5
Answer
Answer: a) 56.2
30. In order to save time in calculating mean from a data set containing a large no: of observations we use ____________
a) Direct method
b) Assumed Mean
c) Both A and B
d) None
Answer
Answer: b) Assumed Mean
Statistical Tools and Interpretation MCQs Class 11 Economics – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode
31. Which Quartile is called Median?
a) Q₀
b) Q₁
c) Q₂
d) None
Answer
Answer: c) Q₂
32. For a symmetrical distribution Q₁ and Q₃ are 30, 90 respectively. The value of median is ___________
a) 30
b) 60
c) 90
d) 40
Answer
Answer: b) 60
33. Mode = _________
a) 3 Median % 2 Mean
b) 3 Median ÷ 2 Mean
c) 3 Median x 2 Mean
d) 3 Median – 2 Mean
Answer
Answer: d) 3 Median – 2 Mean
34. Median can be calculated from _________
a) Individual Series
b) Discrete Series
c) Continuous Series
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
35. Which of the following is not a mathematical average?
a) Arithmetic Mean
b) Harmonic Mean
c) Geometric Mean
d) None
Answer
Answer: d) None
Term 1 – NCERT Economics Class 11 MCQ
Part A – MCQ Questions for Class 11 Statistics Economics
- Introduction to Statistics Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Collection, Organisation and Presentation of Data
- Statistical Tools and Interpretation – Arithmetic Mean, Median and Mode
Part B – MCQ Questions for Class 11 Microeconomics